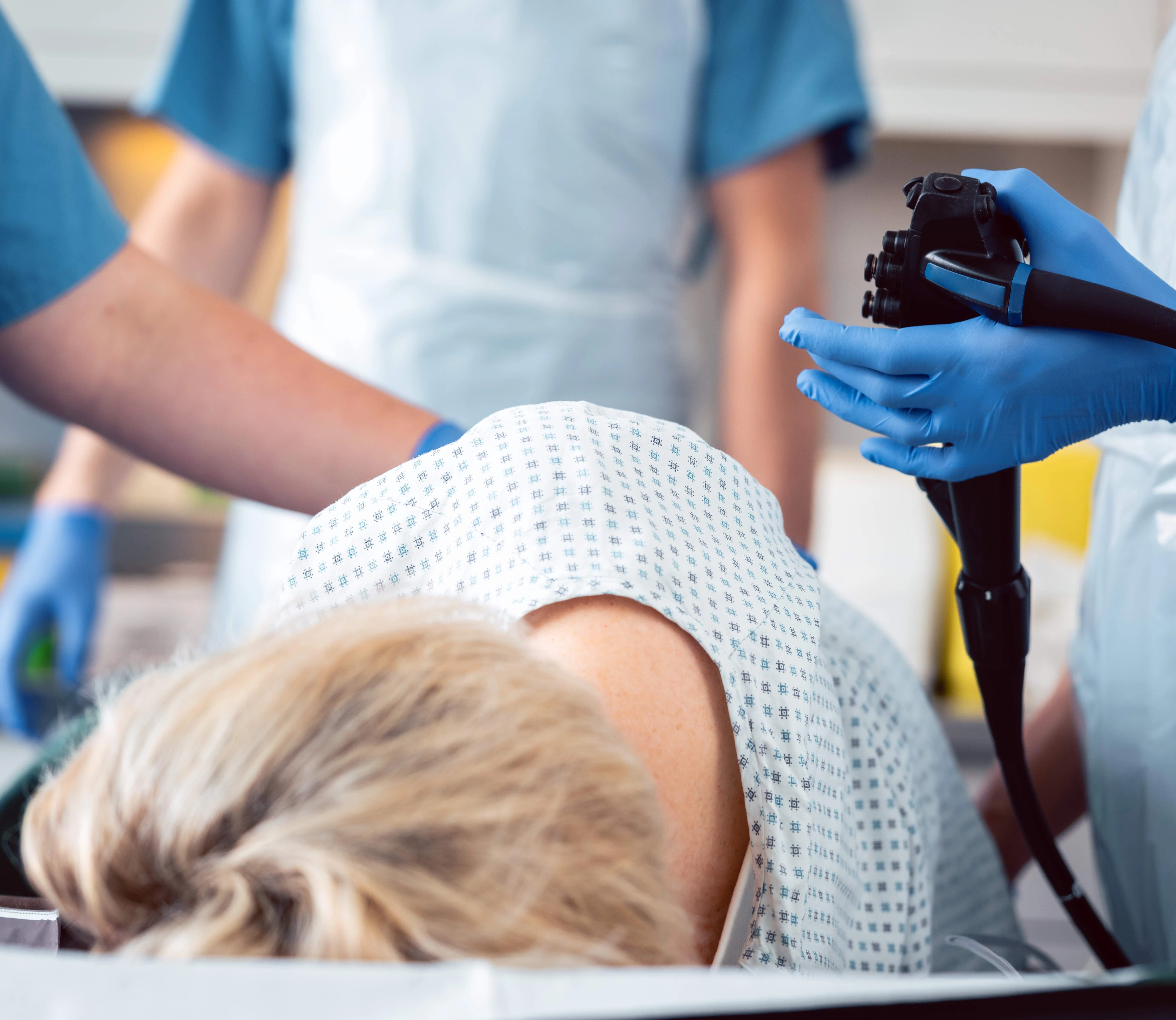
For the examination, the patient is laid on their left side, covered with a blanket, and asked to pull his pants down to the knees, then he turns on his side and pulls his knees up to his stomach. The examination is performed after an intravenous anesthetic and a hypnotic agent is administered, the patient sleeps throughout the examination and shortly afterward.
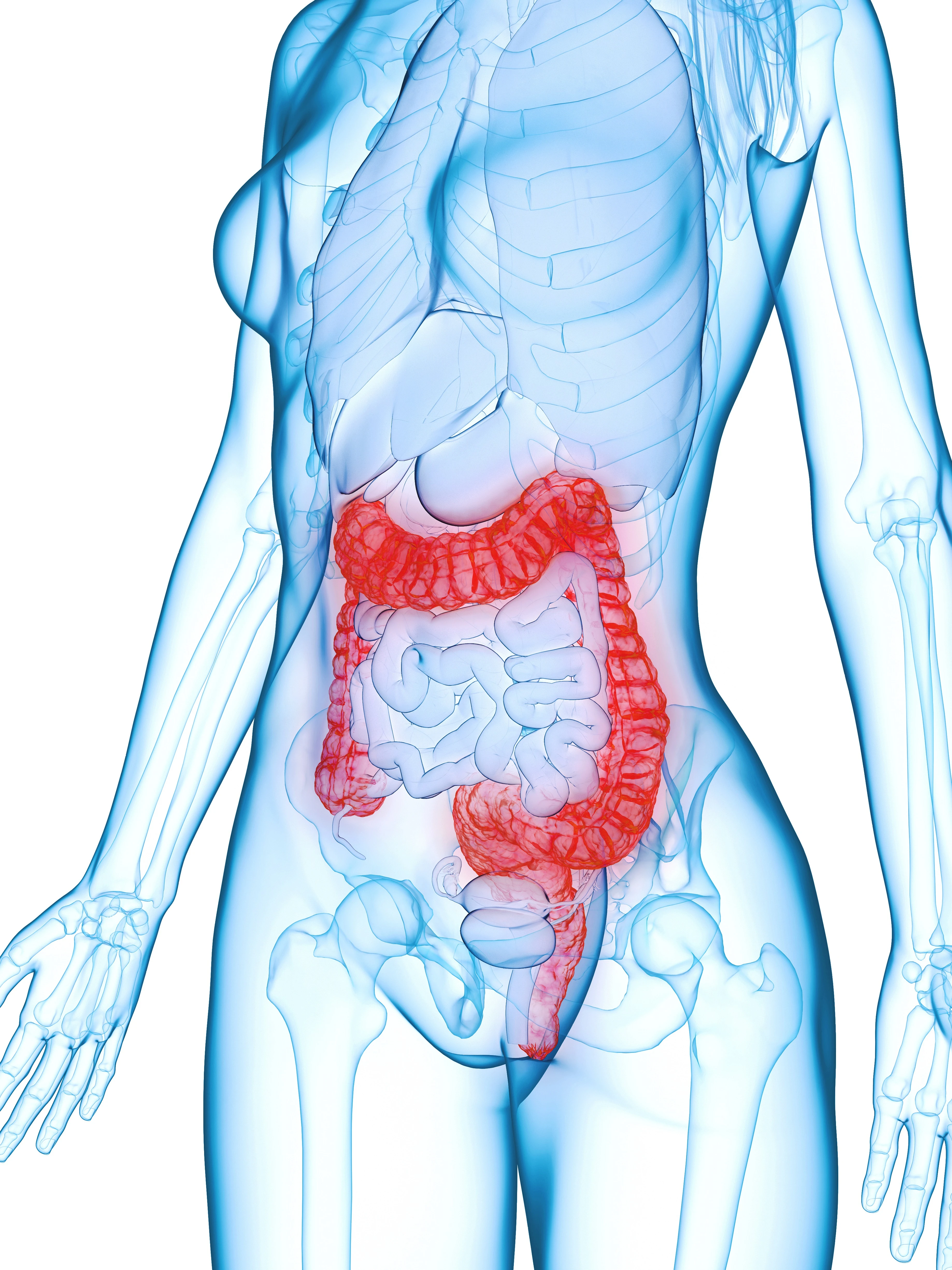
The examination itself is performed using a flexible colonoscope, which is inserted through the anus into the large intestine. Air is blown during the examination to make the walls of the colon more visible, which may cause some slight discomfort and gas evacuation after the examination.
If a site within the part of the digestive tract that is being examined raises suspicions, a microscopic piece (biopsy) of that area will be taken for laboratory testing.
If polyps are found within the section of the intestine being inspected, they can be removed using a special loop inserted through the colonoscope (polypectomy). However, it should be remembered that there are not always direct indications for this (e.g. when polyps do not arouse the doctor's suspicions), and removal of polyps may not be possible during an outpatient examination - then you will be referred to a hospital for surgery with the possibility of observation after its procedure.
The examination lasts from 10 to 30 minutes, depending on its complexity, the number of biopsies taken, and possible polypectomy.
The examiner will inform you about the results of the colonoscopy and will issue a description immediately after the examination. If samples have been taken for histopathological examination, the results will be available for up to 6 weeks.
Book a Visit