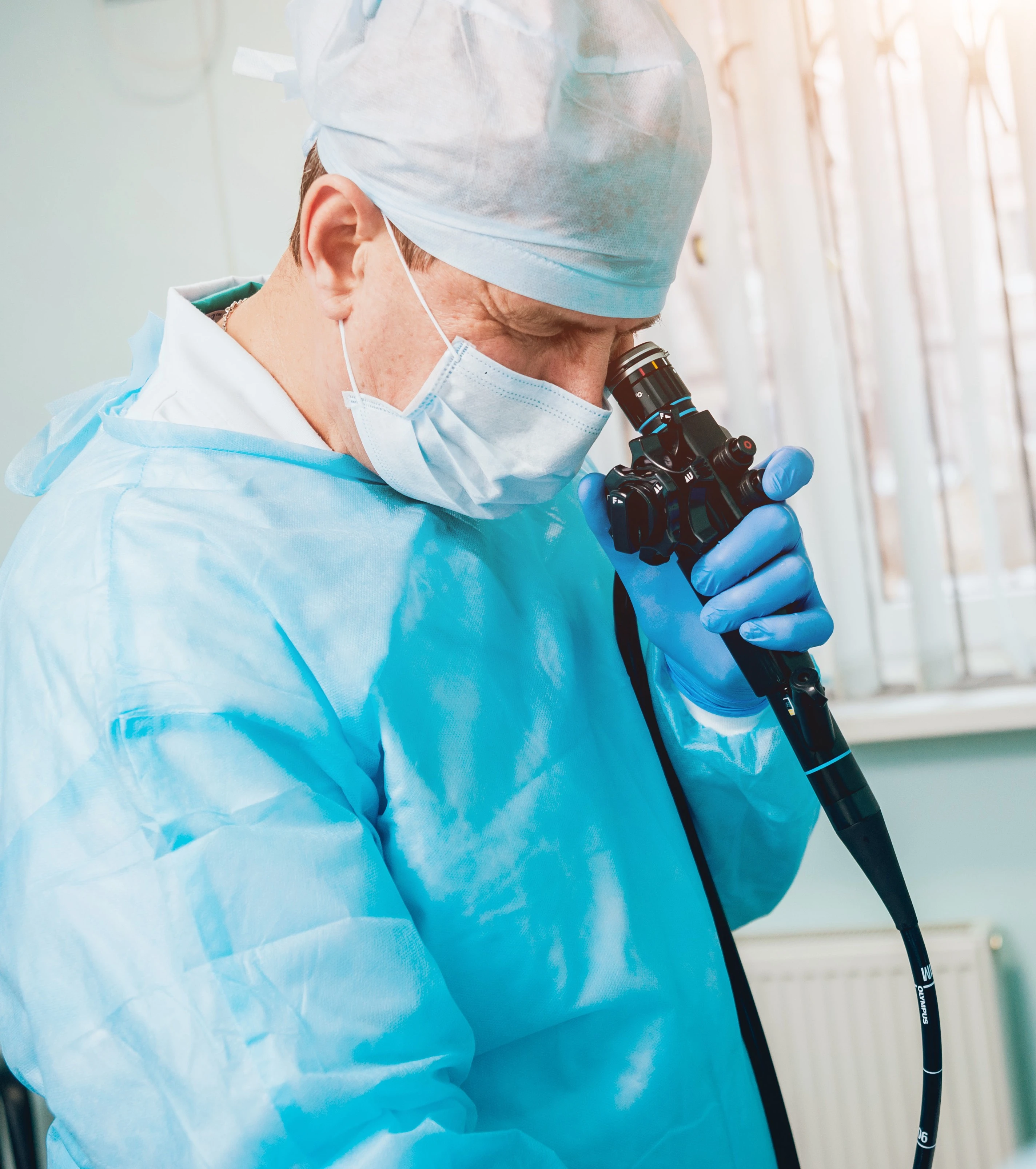
A sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the final section of the large intestine. It allows using a flexible finger-thick device equipped with an optical fiber to assess the inside of the large intestine. The sigmoidoscope includes several small tunnels. One of these tunnels is used to suck in the mucoid fluid encountered during the exploration. The second tunnel is used during sigmoidoscopy to collect material for biopsy.
A sigmoidoscope allows you to examine the final section of the large intestine - the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and the rectum. The doctor who performs the examination has a control device in his hand that allows them to control the tip of the sigmoidoscope inserted in the intestine. During the examination, if bowel changes are found, specimens are taken for histopathological examination. The patient receives the test result after about 6 weeks and further treatment depends on the result.
In the case of many diseases, sigmoidoscopy is the best way to make an accurate diagnosis.