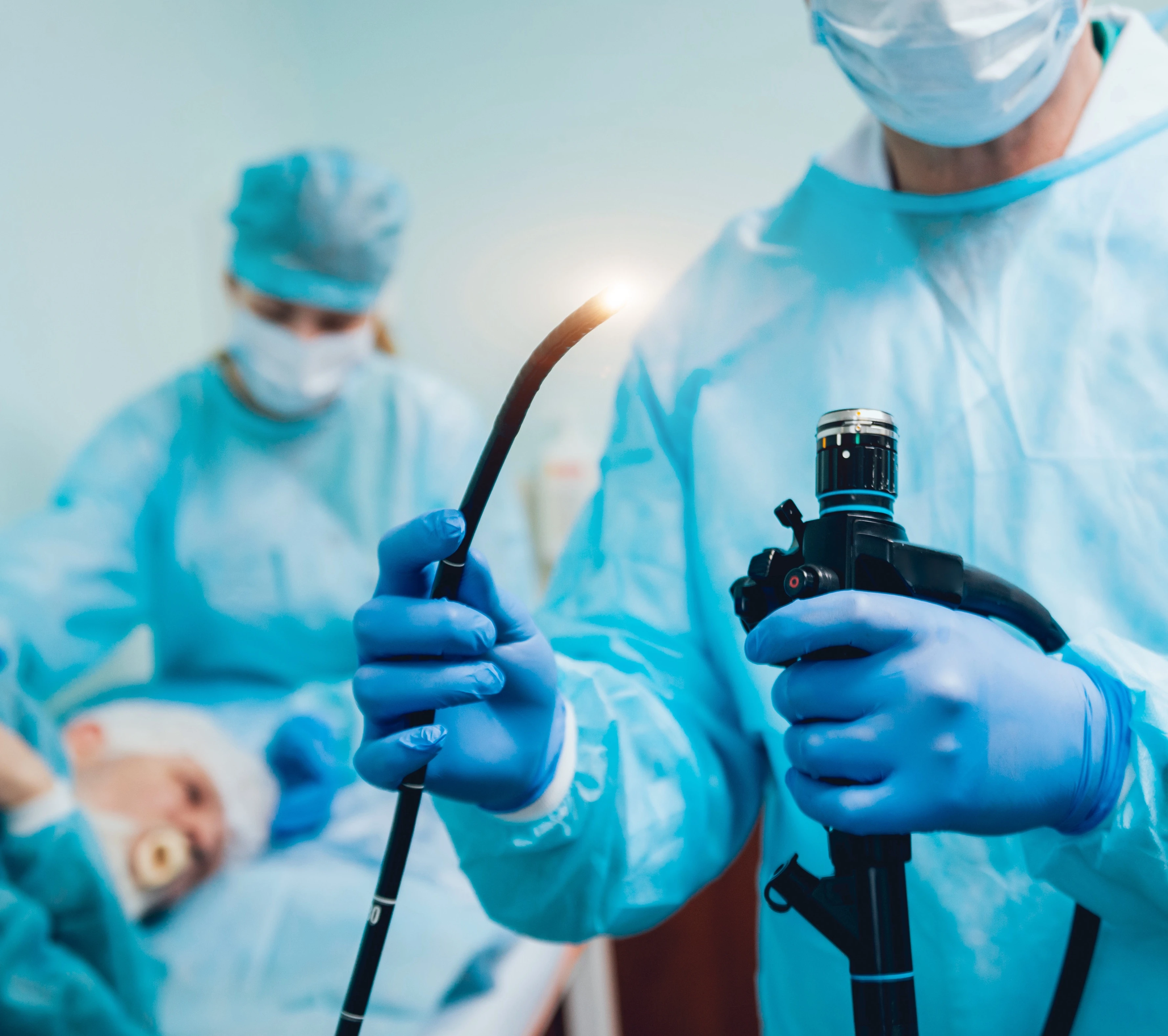
The patient is laid on the bed on the left side and the inside of the mouth and throat is sprayed with a local anesthetic. In the case of intravenous anesthesia (sedation), this step will be omitted, and instead, the patient will be given a catheter and drugs with an anesthetic and sedative effect.
The gastroscope is inserted directly into the throat, continuing into the esophagus, which is also examined, and finally reaches the stomach and finally the first part of the small intestine - the duodenum.
Insertion of the gastroscope into the stomach after local anesthesia may cause the patient discomfort and a sensation of inhibited breathing, but these can be managed by breathing deeply and calmly through the nose throughout the examination.
During the examination, the air is blown through the gastroscope to better visualize the wall of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum, which may cause discomfort during the examination but does not cause pain or impede breathing. The tip of the gastroscope inside the stomach can be rotated in all directions, which allows you to inspect the walls of this organ very carefully.
If a site raises suspicions within the examined upper gastrointestinal tract, a microscopic piece (biopsy) of that area will be taken for laboratory testing, which is not painful.
When the examination is completed, the gastroscope is pulled out. The examination takes about 5-10 minutes and may cause temporary discomfort, but does not impede breathing. After the examination, you may experience distention and belching for a short time.
If a local anesthetic has been used, you should not eat or drink anything for two hours, but you may return to your daily activities immediately.
The description of the gastroscopy is issued to the patient after the end of the examination, if biopsies have been taken for histopathological examination, you will have to wait up to 6 weeks for their result.